往期刊物2015
卷册: 5, 期号: 9
生物化学
Protein Extraction from Drosophila Embryos and Ovaries
从果蝇胚胎和卵巢提取蛋白质
微生物学
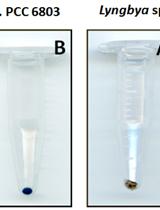
Measurement of Chlorophyll a and Carotenoids Concentration in Cyanobacteria
蓝藻细菌中叶绿素a和类胡萝卜素浓度的测量
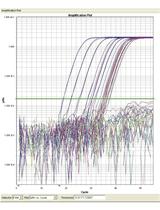
Quantification of HIV RNA and Human Herpesvirus DNA in Seminal Plasma
精浆中HIV RNA 和人疱疹病毒DNA的量化
分子生物学
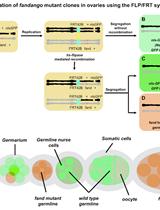
FLP/FRT Induction of Mitotic Recombination in Drosophila Germline
果蝇种系中有丝分裂重组的FLP/FRT诱导
神经科学
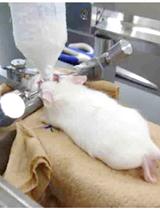
ELISA Detection of Endogenous Serum Albumin in the Mouse Brain: A Measure of Extravasation Following Brain Injury
脑损伤后外渗的一种检测方法:酶联免疫吸附试验检测小鼠脑内血清白蛋白
植物科学
Chlorophyll Fluorescence Measurements in Arabidopsis Plants Using a Pulse-amplitude-modulated (PAM) Fluorometer
采用脉冲调幅(PAM)荧光计测定拟南芥植株的叶绿素荧光
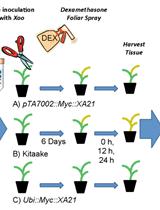
The Use of a Dexamethasone-inducible System to Synchronize Xa21 Expression to Study Rice Immunity
使用地塞米松诱导系统同步Xa21表达进行水稻免疫研究
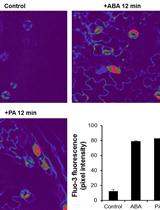
A Protocol to Measure the Cytoplasmic Calcium in Arabidopsis Guard Cells
一种测定拟南芥保卫细胞中胞质钙离子的方法
Quantification of Ralstonia solanacearum Colonization of Potato Germplasm Using Luminescence
发光法定量测定马铃薯种质中青枯菌的定植
MIFE Technique-based Screening for Mesophyll K+ Retention for Crop Breeding for Salinity Tolerance
采用MIFE技术筛选持K+叶肉用于耐盐作物的育种
An Assay to Test Manganese Tolerance in Arabidopsis
拟南芥的耐锰实验分析
Arabidopsis Metabolome Analysis Using Infusion ESI FT-ICR/MS
融合ESI FT-ICR/MS法分析拟南芥代谢组
干细胞
Glioma Associated Stem Cells (GASCs) Isolation and Culture
胶质瘤相关干细胞(GASC)的分离和培养