往期刊物2018
卷册: 8, 期号: 11
生物化学
Preparation of Lipid-Stripped Serum for the Study of Lipid Metabolism in Cell Culture
用于细胞培养中脂质代谢研究的去脂质血清的制备
癌症生物学
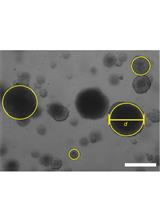
3D Culture Protocol for Testing Gene Knockdown Efficiency and Cell Line Derivation
用于检测基因敲减效率和细胞系建立3D培养方法
Hyaluronan Isolation from Mouse Mammary Gland
小鼠乳腺中透明质酸的分离
发育生物学
In vitro Osteoclastogenesis Assays Using Primary Mouse Bone Marrow Cells
原代小鼠骨髓细胞诱导生成体外破骨细胞试验
微生物学
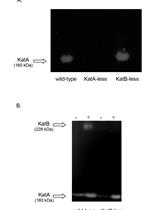
Detection of Catalase Activity by Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) in Cell Extracts from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(PAGE)检测铜绿假单胞菌细胞提取物中的过氧化氢酶活性
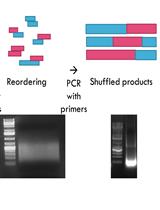
Characterization of Protein Domain Function via in vitro DNA Shuffling
通过体外DNA混洗技术鉴定蛋白质域功能
分子生物学
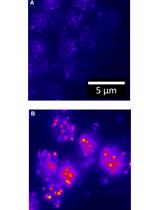
Single-probe RNA FISH in Yeast
酵母菌单探针 RNA FISH
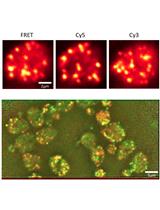
Dual-probe RNA FRET-FISH in Yeast
酵母菌双探针RNA FRET-FISH
神经科学
Intracellular and Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Measurement in Primary Cultured Neurons
原代培养的神经元细胞和线粒体中活性氧的测定
The Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP): A Spatial Navigation Task for Rats
旅行商问题(TSP):大鼠空间导航任务
植物科学
Protocol for RYMV Inoculation and Resistance Evaluation in Rice Seedlings
水稻幼苗RYMV接种和抗性评估方法
Slow and Fast Desiccation of Single-cell Thick Fronds of Filmy Ferns
膜蕨类植物单细胞厚叶状体的缓慢及快速干燥
干细胞
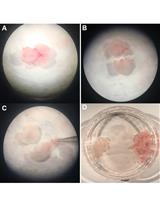
Expansion of Airway Basal Cells and Generation of Polarized Epithelium
气道基底细胞扩增和极化上皮细胞生成