往期刊物2017
卷册: 7, 期号: 11

生物化学
Heavy Metal Stress Assay of Caenorhabditis elegans
秀丽隐杆线虫重金属胁迫检测
癌症生物学
DNA Fiber Assay upon Treatment with Ultraviolet Radiations
紫外线辐射处理后DNA纤维的检测
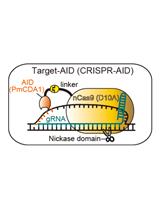
Targeted Nucleotide Substitution in Mammalian Cell by Target-AID
在哺乳动物细胞中通过靶向性AID进行核苷酸靶向置换
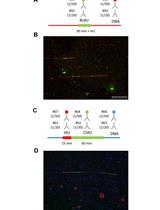
Single-molecule Analysis of DNA Replication Dynamics in Budding Yeast and Human Cells by DNA Combing
采用DNA梳理技术对芽殖酵母和人类细胞中DNA复制动力学进行单分子分析
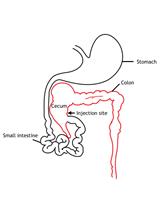
Intracaecal Orthotopic Colorectal Cancer Xenograft Mouse Model
脑内原位结直肠癌异种移植小鼠模型
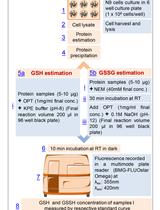
Fluorometric Estimation of Glutathione in Cultured Microglial Cell Lysate
培养的小胶质细胞裂解液中谷胱甘肽的荧光法估测
Pituitary Isograft Transplantation in Mice
小鼠垂体同系移植物移植
Whole Mammary Gland Transplantation in Mice Protocol
小鼠全乳腺移植方案
细胞生物学
Generation of Mutant Pigs by Direct Pronuclear Microinjection of CRISPR/Cas9 Plasmid Vectors
通过直接原核显微注射CRISPR/Cas9质粒载体生成突变株
Flow Cytometric Analysis of HIV-1 Transcriptional Activity in Response to shRNA Knockdown in A2 and A72 J-Lat Cell Lines
A2和A72 J-Lat细胞系中HIV-1经shRNA沉默后转录活性的流式细胞分析
免疫学
ELISPOT Assay to Measure Peptide-specific IFN-γ Production
采用ELISPOT测定法测定肽特异性IFN-γ的生成
In vitro Antigen-presentation Assay for Self- and Microbial-derived Antigens
自身抗原和微生物源性抗原的体外抗原呈递测定
Isolation and Infection of Drosophila Primary Hemocytes
果蝇原代血细胞的分离和感染
微生物学
Expression and Purification of the Cas10-Csm Complex from Staphylococci
表达并纯化葡萄球菌的Cas10-Csm复合体
A Reliable Assay to Evaluate the Virulence of Aspergillus nidulans Using the Alternative Animal Model Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera)
以大蜡螟(鳞翅目)为动物替代模型评估构巢曲霉毒力的可靠实验方法
Fluorescently Labelled Aerolysin (FLAER) Labelling of Candida albicans Cells
使用荧光标记的嗜水气单胞菌溶素变异体(FLAER)标记白色念珠菌细胞
Phototaxis Assays of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 at Macroscopic and Microscopic Scales
宏观和微观尺度上集胞藻PCC 6803的趋光性分析
Induction and Quantification of Patulin Production in Penicillium Species
青霉菌展青霉素生成的诱导和定量
Protein Localization in the Cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC7120 Using Immunofluorescence Labeling
免疫荧光标记定位蓝藻鱼腥藻属PCC7120中的蛋白质
Ex vivo Model of Human Aortic Valve Bacterial Colonization
人类主动脉瓣膜细菌定植离体模型
分子生物学
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Experiments from Whole Drosophila Embryos or Larval Imaginal Discs
整个果蝇胚胎或幼虫成虫盘的染色质免疫沉淀实验
A Protocol for Production of Mutant Mice Using Chemically Synthesized crRNA/tracrRNA with Cas9 Nickase and FokI-dCas9
利用化学合成的crRNA/tracrRNA-Cas9 Nick酶及FokI-dCas9产生突变小鼠的实验方法
Formation of Minimised Hairpin Template-transcribing Dumbbell Vectors for Small RNA Expression
用于小分子RNA表达的最小化发夹模板转录哑铃形载体生成
神经科学
Kinetic Lactate Dehydrogenase Assay for Detection of Cell Damage in Primary Neuronal Cell Cultures
采用乳酸脱氢酶动力测定法检测原代神经元细胞培养物中的细胞损伤
The Repeated Flurothyl Seizure Model in Mice
三氟乙醚诱导的小鼠反复癫痫发作模型
植物科学
DNA-free Genome Editing of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Using CRISPR and Subsequent Mutant Analysis
利用CRISPR技术对莱茵衣藻进行DNA-free的基因组编并对产生突变进行分析
Protocol for Enrichment of the Membrane Proteome of Mature Tomato Pollen
成熟番茄花粉膜蛋白质组富集实验
Determining Genome Size from Spores of Seedless Vascular Plants
无种子维管束植物孢子基因组大小的测定
Photometric Assays for Chloroplast Movement Responses to Blue Light
光度法测定叶绿体对蓝光的运动反应
Whole-seed Immunolabeling of Arabidopsis Mucilage Polysaccharides
拟南芥粘液多糖的全种子免疫标记
干细胞
Functional Analysis of Connexin Channels in Cultured Cells by Neurobiotin Injection and Visualization
通过神经生物素注射和可视化对培养细胞中连接蛋白通道进行功能分析