往期刊物2014
卷册: 4, 期号: 19
癌症生物学
Hypoxia Studies with Pimonidazole in vivo
体内哌莫硝唑缺氧研究
免疫学
Coagulation Assay
血细胞凝集试验
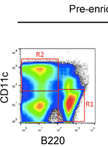
Isolation and in vivo Transfer of Antigen Presenting Cells
抗原递呈细胞的分离和体内转移
微生物学
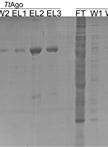
Expression and Purification of the Thermus thermophilus Argonaute Protein
嗜热细菌Argonaute蛋白的表达和纯化
Construction of Glycine Oxidase Mutant Libraries by Random Mutagenesis, Site Directed Mutagenesis and DNA Shuffling
通过随机突变、点位定向诱变和DNA改组构建甘氨酸氧化酶突变库
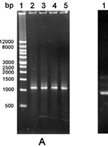
Chromogenic Substrate Assay for Determining the Activity of Plasma Kallikrein
显色底物分析测定血浆激肽释放酶活性
神经科学
Novel Object Recognition for Studying Memory in Mice
采用新物体识别研究小鼠的记忆
In utero Electroporation of the Embryonic Mouse Retina
小鼠子宫内胚胎视网膜DNA电转移
Two-choice Digging Task in Mouse for Studying the Cognitive Flexibility
采用小鼠双选择挖掘任务研究认知灵活性
植物科学
Carotenoid Extraction and Quantification from Capsicum annuum
甜椒中的类胡萝卜素提取和定量测定
Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated Transformation of Walnut (Juglans regia)
农杆菌介导的核桃转化
Endogenous ABA Extraction and Measurement from Arabidopsis Leaves
拟南芥叶片中内源ABA的提取和测定
Localisation and Quantification of Reactive Oxygen Species and Nitric Oxide in Arabidopsis Roots in Response to Fungal Infection
拟南芥根部响应真菌感染的活性氧和一氧化氮的定位和定量测定
Pea Aphid Survival Assays on Arabidopsis thaliana
拟南芥的豌豆蚜存活实验
Analysis of Total Se Content in Rice
水稻中总硒含量的分析