往期刊物2014
卷册: 4, 期号: 15
生物化学
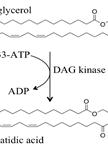
Quantitative Analysis of Cellular Diacylglycerol Content
细胞中甘油二酯含量的量化分析
免疫学
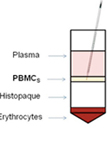
Generation and Maturation of Human Monocyte-derived DCs
由人单核细胞诱导树突细胞的产生和成熟
微生物学
Purification of Herpesvirus Virions and Capsids
疱疹病毒和病毒衣壳的纯化
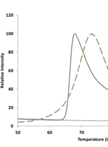
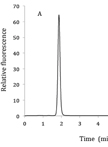
Fluorometric Estimation of Viral Thermal Stability
荧光法预测病毒热稳定性
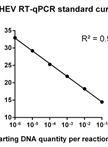
Infectious Virus Yield Assay for Hepatitis E Virus
戊型肝炎病毒的感染病毒产量分析
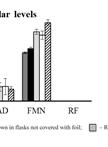
Quantification of Flavin Production by Bacteria
细菌黄素产量的定量测定
Luminescence-based Antiviral Assay for Hepatitis E Virus
针对戊型肝炎病毒的发光抗病毒物质试验
Assay for GTP Cyclohydrolase II Activity in Bacterial Extracts
细菌提取物中GTP环化水解酶II活性分析
植物科学
DNA Fragmentation Analysis
DNA片段化分析
Floral Dip Transformation in Lepidium campestre
花器官浸蘸法转化绿独行菜
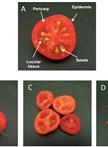
Isolation of Tomato Fruit Chromoplasts and Determination of ATP Levels
番茄果实有色体的分离和ATP含量的测定
Quantifying Fruit Dehiscence Using the Random Impact Test (RIT)
采用随机碰撞试验(RIT)定量测定果实开裂